A Study of Advection Schemes in OpenFOAM for the Volume of Fluid Method and their Applicability to Atomization
- type:numerical master thesis
- tutor:
Task
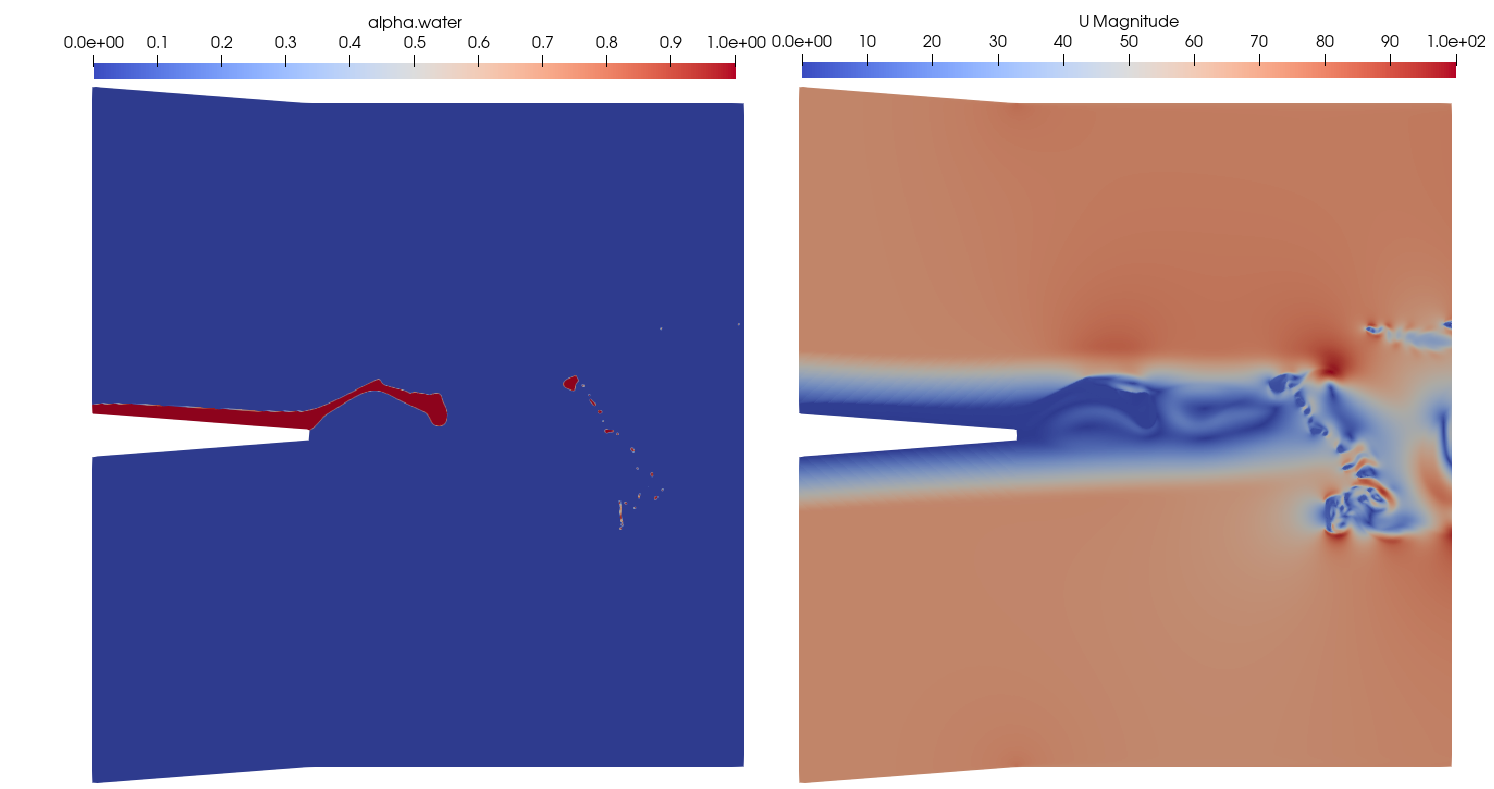
Fuel atomization, the process of breaking liquid fuel into fine droplets for efficient combustion, is a crucial factor in determining the pollution levels of jet engines and is thus an active area of research. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD), specifically the Volume-of-Fluid method (VOF), is a key tool for the prediction of such multiphase flows. In VOF, the advection of the volume fraction is essential for capturing the interface dynamics and thus an accurate prediction of the spray.
In this master thesis, various schemes for the computation of this advection term in the Open-source CFD package OpenFOAM are to be tested and analysed regarding their applicability to atomization. The focus will be on evaluating stability, accuracy, robustness, and computational cost, providing a comprehensive understanding of each scheme's performance under relevant condition
Through this thesis, you will gain hands-on experience with CFD, deepening your understanding of multiphase flow simulations, and develop skills in analysing numerical schemes. As OpenFOAM is one of the most widely used CFD-packages in both research and industry, this thesis will be an ideal preparation for a continued career in the field of computational fluid dynamics.